
by Rouema B. Peralta-Perez, MD, MMHeA, FPAFP


by Rouema B. Peralta-Perez, MD, MMHeA, FPAFP
Learn why zinc is a vital nutrient and the benefits that come with incorporating it into your everyday to improve your health.
Zinc gluconate, a popular zinc supplement, has gained attention for its excellent absorption and effectiveness. Made by combining zinc with gluconic acid, zinc gluconate offers a reliable source of this essential mineral. Zinc itself plays a critical role in numerous bodily functions, from supporting the immune system to aiding in wound healing. In this article, we’ll explore the importance of zinc, the benefits of zinc gluconate supplementation, and the recommended daily intake for optimal health.

Zinc is an essential trace mineral that is involved in many physiological processes. Although it is required only in small amounts, its role is indispensable in various systems of the body.

Zinc is a key player in maintaining a healthy immune system. It supports the production of immune cells and helps the body fight infections. Specifically, zinc is critical for the normal development and function of immune cells such as neutrophils and natural killer cells. These cells are essential in the body’s defense against pathogens. Furthermore, zinc helps maintain the integrity of the skin and mucous membranes, which act as barriers to infection, preventing harmful bacteria and viruses from entering the body.

Zinc’s contribution to skin health cannot be overstated. It plays a crucial role in wound healing by promoting new cell growth and aiding in the repair and regeneration of skin cells. This makes it an important element in the recovery process after injuries, cuts, or burns. Individuals with zinc deficiency often experience delayed wound healing, further emphasizing its role in skin repair.

Zinc is involved in the formation of DNA and proteins, processes that are fundamental for cell growth and tissue repair. It is essential for DNA replication and cell division, making it critical for growth, development, and wound healing. Zinc deficiency can impair cell division, leading to various health complications, including stunted growth in children and poor recovery from injuries.

An often overlooked but important function of zinc is its role in taste and smell. Zinc deficiency can lead to a diminished sense of these senses. This can affect appetite and overall nutrition, especially in older adults. By ensuring adequate zinc intake, individuals can maintain their ability to taste and smell, contributing to overall well-being.

Zinc also functions as an antioxidant, helping to stabilize proteins and cell membranes, thus protecting the body from oxidative stress. Free radicals, which are unstable molecules that can damage cells, are neutralized by zinc, preventing cellular damage. This makes zinc an important factor in protecting the body from conditions linked to oxidative stress, such as chronic inflammation and aging-related diseases

Zinc gluconate has been extensively studied, and its benefits are well-documented. Here are some of the key advantages of incorporating zinc gluconate into your health routine:

Several studies have shown that zinc gluconate can reduce the duration of the common cold if taken within 24 hours of the onset of symptoms. By supporting the immune system, zinc helps the body mount a quicker response to the cold virus, shortening the length of illness.

Regular zinc supplementation has been shown to help maintain a healthy immune system, especially in individuals who are prone to frequent infections or those who may be at risk of zinc deficiency. Zinc gluconate can provide consistent immune support, making it a valuable supplement for overall health.

Zinc is essential in the treatment of minor wounds and various skin conditions. It promotes skin cell repair and regeneration, accelerating the healing process. Moreover, its anti-inflammatory properties make it particularly beneficial for treating acne. By reducing sebum production and bacterial growth—two primary contributors to acne—zinc helps prevent and treat breakouts.

Zinc’s role in reducing inflammation extends beyond acne. Its anti-inflammatory properties can be beneficial for various skin conditions, helping to reduce redness, swelling, and irritation. This makes it a versatile supplement for those dealing with chronic skin issues.
The recommended daily allowance (RDA) for zinc varies by age, gender, and life stage. It is important to meet these requirements to avoid both deficiency and excess intake. Below are the RDAs for zinc:
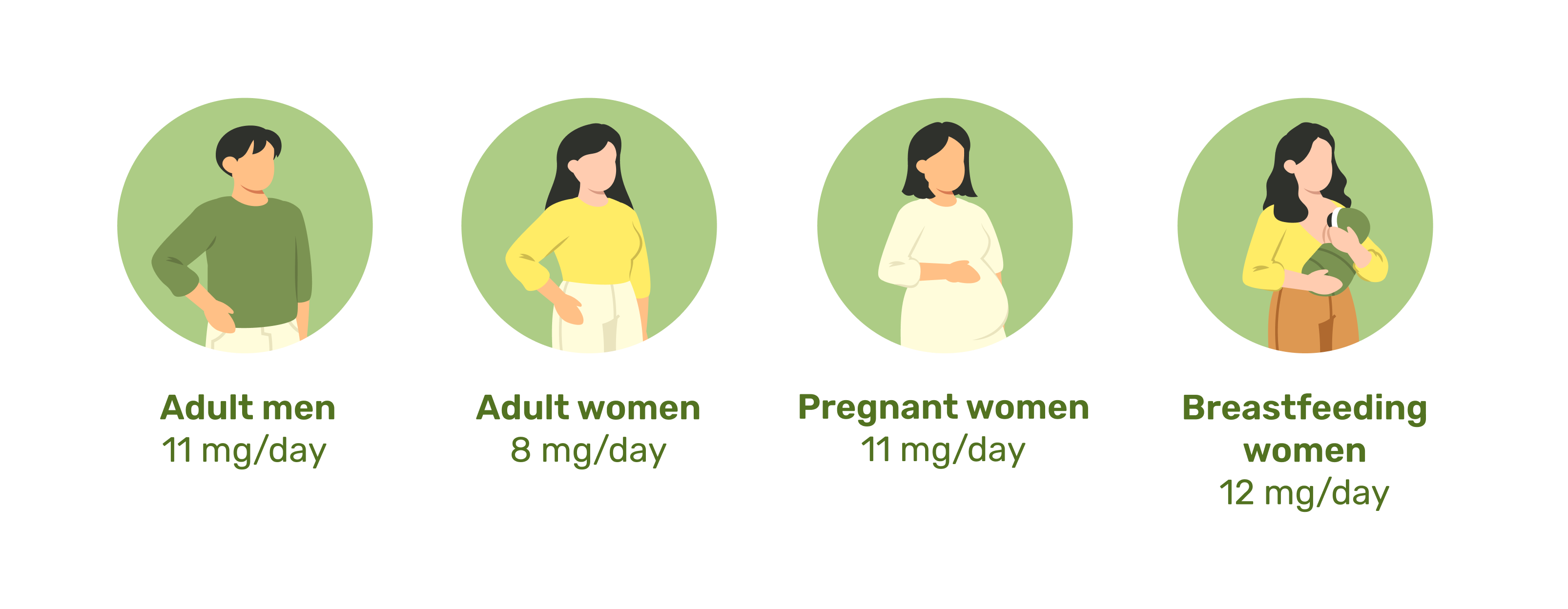
While many people get enough zinc through their diet, certain individuals may benefit from zinc supplementation, particularly those at risk of deficiency. Populations at risk include people with malabsorption disorders, vegetarians, older adults, and individuals with chronic illnesses.

While zinc is essential, too much of it can be harmful. High doses of zinc, especially above the upper limit of 40 mg per day, can lead to side effects such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. Prolonged, excessive intake of zinc can interfere with copper absorption, leading to copper deficiency. This can result in anemia and neurological issues.
Although zinc toxicity is rare, it’s important to stick to the recommended daily intake and avoid excessive supplementation.

If you are concerned about your zinc intake or if you frequently experience colds, poor wound healing, or skin issues, zinc gluconate may be a helpful supplement. However, it is always best to consult with a healthcare provider before adding any supplement to your routine. This is particularly important if you have an underlying health condition or are taking other medications.
In conclusion, zinc gluconate is an effective and well-absorbed form of zinc that offers numerous health benefits. From supporting the immune system to promoting skin health, this essential mineral plays a vital role in maintaining overall well-being. Just remember, balance is key—ensure you meet your body’s zinc needs without overdoing it.
6